Unemployment is a critical issue that affects individuals and economies around the world. Understanding the causes of unemployment is essential for policymakers, economists, and job seekers alike. As we delve into the topic, we will explore the various factors that contribute to this pressing social problem, examining economic, structural, and policy-related causes. The more we know about unemployment: causes, the better equipped we are to address its implications and find sustainable solutions.
Unemployment: Causes Explored
Unemployment can be viewed through different lenses, and by acknowledging its diverse causes, we can tailor our approaches to mitigate its effects. The underlying factors contributing to unemployment can be categorized into several broad categories, including cyclical, frictional, structural, and seasonal unemployment, each with its own implications and potential solutions.
Economic Factors Behind Unemployment: Causes
One of the primary drivers of unemployment is economic conditions. Economic downturns and recessions typically lead to higher unemployment rates as businesses may close their doors or reduce their workforce to cut costs. During such periods, the economy slows down, demand for goods and services diminishes, and companies are forced to make tough decisions.
Cyclical Unemployment: A Major Economic Cause
Cyclical unemployment occurs in relation to the economic cycle. When the economy experiences a recession, businesses reduce their activities, leading to layoffs and job losses. For instance, during the financial crisis of 2008, many industries faced significant downturns. Workers in sectors such as construction, manufacturing, and retail were often the first to lose their jobs, which exemplifies how cyclical unemployment operates. Policymakers often respond to cyclical unemployment with fiscal and monetary policies aimed at stimulating economic growth, encouraging job creation, and supporting those who are out of work.
Understanding Structural Unemployment: Causes
Structural unemployment arises when there is a mismatch between the skills that workers possess and the skills needed by employers. Advances in technology can lead to structural unemployment, as automation and digitization can render certain roles obsolete. Workers in traditional fields may find themselves lacking the necessary skills to transition into new job markets. For example, as manufacturing jobs increasingly automated tasks, individuals without technical skills may struggle to secure employment. Addressing structural unemployment requires a concerted effort on the part of both educational institutions and employers to ensure that workers are equipped with the skills necessary to thrive in a changing economy.
The Impact of Policies on Unemployment: Causes
Government policies also play a significant role in influencing employment rates. Economic policies, labor regulations, and welfare programs can affect both the availability of jobs and the motivation of individuals to seek them.
Labor Policies and Their Contribution to Unemployment: Causes
Labor market policies encompass a wide range of regulations, including minimum wage laws, employee benefits mandates, and unemployment insurance programs. While these policies aim to protect workers, they can also unintentionally lead to higher unemployment. For instance, a significantly high minimum wage may discourage employers from hiring entry-level workers, leading to increased youth unemployment. On the other hand, effective unemployment benefits can provide a safety net for those out of work, allowing them to seek suitable employment rather than accepting the first job that comes their way, which can contribute to structural unemployment if the jobs available do not match their skills.
Seasonal Unemployment: Causes Related to Time
Another facet of unemployment to consider is seasonal unemployment, which occurs at particular times of the year when certain industries slow down or shut down. Industries such as agriculture, tourism, and retail often face this challenge, with hiring and job losses fluctuating throughout seasons and holidays. For example, agricultural workers may find themselves unemployed during the offseason when crops are not cultivated, while retail workers may face reduced hours after the holiday shopping season.
Addressing Seasonal Unemployment: Causes
Addressing seasonal unemployment requires both an understanding of industry cycles and the implementation of supporting practices. Efforts can include diversifying job opportunities within communities so that workers can transition to alternate industries during off-peak times or providing training for skills that can be utilized across seasonal lines. Furthermore, creating policies that encourage year-round employment can help mitigate the impacts of seasonal unemployment.
Unemployment: Causes Linked to Globalization
In today’s interconnected world, globalization has also played a role in shaping unemployment rates across various regions. As companies expand their operations internationally, they may outsource jobs to countries where labor is cheaper. While this can lead to cost savings for businesses, it often results in job losses in the home country and can lead to an increase in unemployment rates. Global trade policies and economic agreements can further exacerbate this issue by making it easier for companies to relocate their operations abroad.
Economic Restructuring and Its Effects on Employment: Causes
The economic restructuring driven by globalization may lead to more retraining initiatives and support programs, helping workers transition into new jobs or industries. Furthermore, promoting growth in emerging sectors that capitalize on globalization, such as technology and services, can create new opportunities for displaced workers. However, finding a balance is critical, as economies must ensure their labor forces are adaptable and equipped to meet the demands of a continuously changing job market.
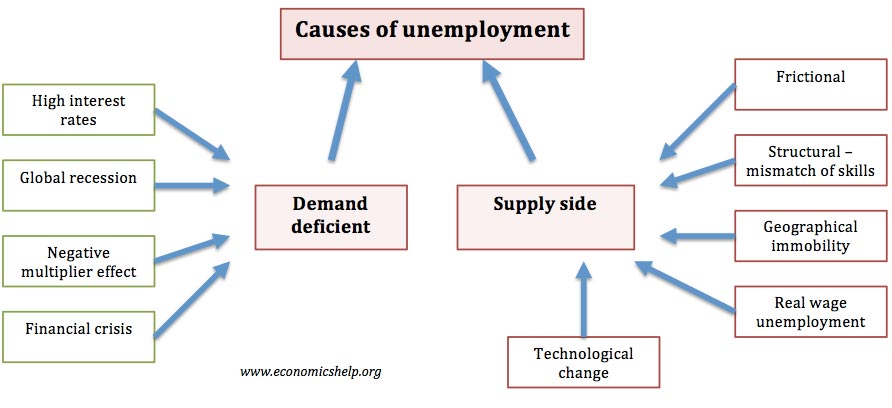
Image Representing Unemployment: Causes
This image visually lays out the various causes of unemployment, serving as a helpful summary of the complex interplay of economic, structural, and policy-related factors discussed above.
The Role of Education in Mitigating Unemployment: Causes
Education undeniably plays a significant role in reducing unemployment rates. A well-educated workforce is typically more adaptable and equipped to meet changing market demands. Moreover, access to education improves individuals’ chances of securing meaningful employment and reduces the likelihood of structural unemployment. Programs that focus on vocational training, apprenticeships, and continued education can help bridge the skill gap and empower individuals to navigate the job market successfully.
Promoting Lifelong Learning to Combat Unemployment: Causes
Promoting lifelong learning is becoming increasingly important as the job market evolves. Encouraging students to acquire a diverse skill set during their education can prepare the next generation for new challenges and opportunities. Furthermore, ongoing training for existing workers can ensure they remain competitive and relevant within their industries.
The responsibility for addressing unemployment: causes extends beyond individuals, requiring collaboration between governments, educational institutions, and private enterprises. Stakeholders must work together to build a robust workforce capable of thriving amidst economic fluctuations and sector shifts.
Final Thoughts on Unemployment: Causes
Unemployment remains a multifaceted challenge that requires a nuanced understanding of its various causes. From economic factors that drive cyclical unemployment to education’s vital role in preventing structural unemployment, addressing these issues requires a well-rounded strategy that takes into account the different dimensions of the problem. As we move forward, a collective effort to adapt, educate, and innovate will be key to reducing unemployment rates and building a stronger economy for all.