Achieving financial independence is a goal that beckons many individuals, representing the ultimate destination in personal finance. The journey towards this independence is not merely about accumulating wealth but involves careful planning and strategic steps. In this article, we’ll explore effective financial independence planning strategies that can pave your way to a more secure and fulfilling life.
Understanding Financial Independence Planning
Financial independence planning is the process of establishing clear financial goals and creating a strategy to achieve them. At its core, it involves gaining control over your money to ensure that your future is secure, regardless of unexpected challenges. To navigate this journey, you must first understand what financial independence means to you personally. Different people may define it in various ways: for some, it could mean retiring early, while for others, it might involve traveling freely without the constraints of a paycheck.
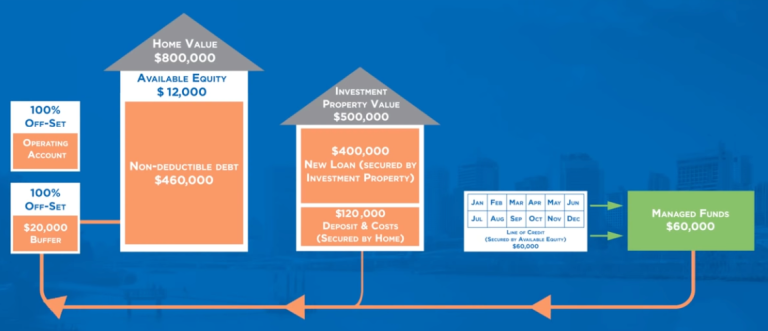
Visual Representation of Financial Independence
This visual highlights the essential steps to take on your journey towards financial independence. It’s crucial to see these steps as interconnected; a robust financial plan will encompass all areas of your finances, including savings, investments, and income generation strategies.
The First Step: Assess Your Current Financial Situation
Before you can begin financial independence planning, you must take a thorough inventory of your current financial standing. This includes understanding your income, expenses, debts, and assets. Here are a few strategies to help you assess your situation effectively:
- Calculate Your Net Worth: Net worth is calculated by subtracting your total liabilities from your total assets. This number gives you a clear snapshot of where you currently stand financially.
- Track Your Spending: Keeping track of your monthly expenses can help identify areas where you might cut back. Use budgeting apps or a simple spreadsheet to categorize and monitor where your money goes.
- Review Your Debts: Understanding the types of debt you have and their corresponding interest rates will help prioritize what to pay off first. Focus on high-interest debts to free up more capital.
Setting Specific Financial Goals
Financial independence planning requires you to set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. For example, instead of saying, “I want to save more,” consider setting a goal like, “I will save $5,000 for an emergency fund within the next year.” Here are some key areas to focus your financial goals on:
- Emergency Fund: Aim to save at least three to six months’ worth of living expenses to protect against unforeseen issues.
- Retirement Fund: Whether through a 401(k), IRA, or other retirement accounts, prioritize contributions to secure your financial future.
- Investing: Research various investment options to grow your wealth over time. The earlier you start, the more you benefit from compound interest.
The Role of Budgeting in Financial Independence Planning
A well-structured budget is a cornerstone of effective financial independence planning. It not only helps manage your spending but also facilitates saving and investing objectives. Here’s how to create a budget that works for you:
- Choose a Budgeting Method: Find a budgeting method that aligns with your lifestyle, whether it’s the envelope system, the 50/30/20 rule, or zero-based budgeting.
- Prioritize Savings: Pay yourself first by allocating a percentage of your income to savings before covering discretionary spending.
- Review and Adjust: Regularly review your budget to make adjustments related to your financial growth and changes in lifestyle.
Diversifying Your Income Streams
In addition to careful budgeting, diversifying your income sources is essential in financial independence planning. Relying solely on one source of income can be risky. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Investing in Real Estate: Real estate can provide both rental income and property value appreciation, giving you a reliable income stream.
- Starting a Side Hustle: Explore your skills and hobbies that can be monetized, whether it’s freelance work, consulting, or selling products online.
- Passive Income Streams: Look into creating passive income through investments like dividend-paying stocks, bonds, or peer-to-peer lending.
Continuous Education: A Key to Financial Independence
Remaining educated and informed is crucial in your journey toward financial independence planning. By continuously increasing your financial knowledge, you can make better decisions. Consider these avenues for personal growth:
- Books: Read books on personal finance and investing to sharpen your financial acumen.
- Courses: Enroll in online courses or attend workshops that cover various financial topics, from budgeting to investing.
- Networking: Engage with communities focused on financial education, whether through online forums or local groups.
Monitoring and Adapting Your Financial Plan
Your journey to financial independence requires ongoing evaluation. Set a regular schedule, such as monthly or quarterly, to review your financial goals and achievements. During this review, consider the following:
- Assess Target Progress: Are you on track to meet your financial goals? If not, recognize patterns or obstacles standing in your way.
- Adapting Strategy: If you are not achieving your goals as expected, be prepared to adjust your plan or approach.
- Celebrate Milestones: Acknowledge your achievements along the way to maintaining motivation and momentum.
The Final Steps to Financial Independence Planning
In closing, remember that financial independence planning is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Tailor your strategies to fit your life circumstances and goals. The road to financial independence is filled with opportunities for learning, adapting, and growing. As you take these steps toward financial independence, remain patient and resilient. Your dedication will lead you toward a future where you have the freedom to make choices based on desires rather than financial limitations.